The Longer Comic: Inflammation — A Slow Burn with Impressive Consequences
Introduction
Inflammation Unveiled: The body’s approach to injury, infection, or harmful stimuli is an inflammatory response. It is a very important and necessary order of the body’s immune defense system because it aids in eliminating harmful agents and also promotes healing.
Nonetheless inflammation that becomes excessive or chronic can cause diseases such as arthritis, cardiovascular diseases, or even autoimmune disorders.
The purpose of this article is to provide the audience with inflammation, its types, causes and symptoms, its mechanisms as well as potent possible treatments.
What is Inflammation?
“Inflammation is the way in which the immune system deals with harmful stimuli of a biological nature such as pathogens, toxic compounds, or damaged cells. It’s essential to the body’s healing process and serves as the first line of defense. However, it can become prolonged and thus contribute to chronic health conditions.”
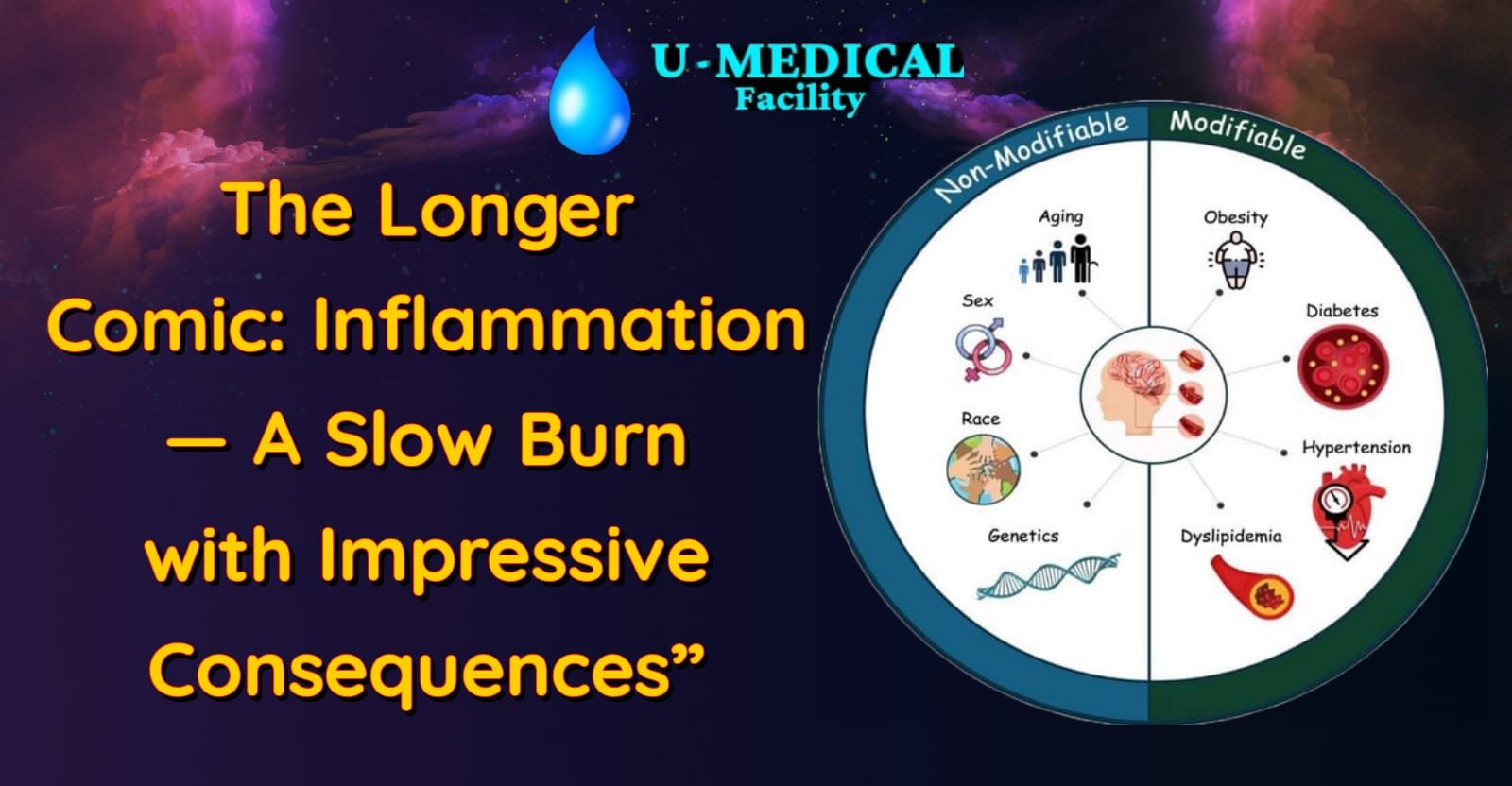
Acute Inflammation symptoms:
1. Redness
2. Swelling
3. Pain
4. Area affected feels hot
5. Loss of Function
Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is characterized by a long-term immune response that stretches over months or years and is often the aftermath of a stubborn infection, autoimmune problems, or recurring exposure to ailments. Read more..
Reasons behind chronic inflammation:
1. Autoimmune conditions like arthritis or lupus
2. Infections like tuberculosis and hepatitis
3. Unceasing stress
4. Obesity along with poor quality food done dietirsts recommend eaters
5. Alcohol and tobacco usage
Chronic Inflammation symptoms:
1. Extreme fatigue
2. Continuous severe discomfort
3. Digestive deficiency hence constipation or diarrhea, or both.
4. Skin legions or other issues and infections popping constantly
Inflammation Mechanism:
The inflammation mechanism involves a series of immunological, vascular, and metabolic events that are progressively organized in order to repair and restore the function of affected tissues.
1. Action Requiring Shift:
An inflammatory response is generated when the body perceives a harmful stimulus such as bacterial infection, viruses, or damaged cells unleashing the immune system.
2. Inflammation Mediator Release:
Your immune system discharges chemicals simplicity to dry cytokines and prostaglandins which seek out white blood cells to the area affected. As a result, they attract white blood cells to protect the area. At this stage, inflammatory mediators induce severe discomfort, redness, and swelling.
3. Elevated Temperature and Increase in Body’s Fluid Levels:
Blood vessels start to broaden, allowing immune cells to access the injury site. This results in increased warmth in the body and blood vessels. Besides, fluid concentration is heightened, permitting proteins, and fluids to pour into tissues. This leads to increased swelling.
4. Recruitment of Immune Cells
White blood cells, particularly neutrophils and macrophages, arrive to neutralize the threats. Neutrophils engulf the bacteria while macrophages clear the dead cells and debris.
5. Resolution and Healing
At its onset, the immune system sends anti-inflammatory signals to quell the issue and encourage repair of tissue. The resolution of this phase is where chronic inflammations goes astray which results in a constant activation of immune system.
Common Diseases Linked to Chronic Inflammation
1. Cardiovascular Diseases
Chronic inflammation contributes to cardiovascular disease by injuring the blood vessels and increasing the deposition of plaques, which results in atherosclerosis.
2. Autoimmune Disorders
Take for example, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis which have their etiology in the immune system that mistakenly attacks the own body tissues.
3. Diabetes
Obesity and poor diet are the leading causes of inflammation which in turn can result in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
4. Cancer
Chronic inflammation is conducive to tumor development through DNA damage and functional alteration of the cell. Chronic hepatitis is an increased risk factor for liver cancer.
5. Neurodegenerative Disorders
Inflammation in the brain has been observed in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, where immune cells identify neurons as their enemies.
Factors That Contribute to Chronic Inflammation
Several lifestyle and environmental factors can worsen or trigger chronic inflammation.
1. Poor Diet
Processes foods, high sugar intake, and trans fats are the most common dietary triggers for increased inflammatory markers.
2. Lack of Exercise
A sedentary lifestyle contributes to obesity and metabolic disorders that promote Inflammation Unveiled
3.Stress
Chronic stress raises cortisol levels, which subsequently alters the immune response and keeps inflammation locked up.
4. Smoking and Alcohol Consumption
Both these smoking as well as the excessive consumption of alcohol lead to tissue damage and trigger inflammatory pathways. Inflammation Unveiled
5. Environmental Toxins
Long-term inflammatory responses can be triggered by exposure to pollutants, chemicals, and allergens.
How to Reduce Inflammation Naturally
Managing inflammation involves lifestyle changes, diet modifications, and medical interventions.
1. Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Some foods have the ability to reduce chronic inflammation with these examples of their anti-inflammatory properties:
Fruits and Vegetables: Berries, leafy greens, tomatoes, and bell peppers are rich in antioxidants.
Healthy Fats: Olive oil, nuts, avocados and fatty fish (salmon, mackerel) which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, and oats stabilize blood sugar levels and also reduce inflammation.
Herbs and Spices: Turmeric, ginger and garlic are very effective against Inflammation Unveiled to the fact that they do not cause any side effects.
2. Regular Exercise
Such types of exercise as walking, yoga or swimming have an intermediate level impact on immune system and inflammation markers.
3. Stress Management
Meditation, deep breathing exercises, and good sleep contribute to excellent health and lower levels of inflammation.
4. Avoiding Harmful Habits
Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake significantly reduce inflammatory responses.
5. Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Obesity is a precursor to chronic Inflammation Unveiled. Proper diet and regular exercise maintain weight control.
Medical Treatments for Inflammation
For severe cases, doctors may recommend medications to control inflammation:
1. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)Ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen reduce pain and Inflammation Unveiled
Commonly used for arthritis, injuries, and mild chronic inflammation.
2. Corticosteroids
Powerful anti-inflammatory drugs like prednisone suppress immune responses.
Used for severe autoimmune diseases and asthma.
Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drug (DMARD)
Medications such as methotrexate and biologics (TNF inhibitors) treat autoimmune disorders.
Antibiotics or Antivirals And if inflammation is caused by an infection, doctors might write prescriptions for antibiotics or antivirals. Click here…
Conclusion
Despite inflammation being an important immune process that facilitates a normal and protective reaction from the body, leaving inflammation unchecked can cause chronic illness.
Knowing what causes inflammation, what its signs and symptoms are, and how inflammation works can help you manage it more effectively.